ISO9001Certified Enterprises National High-tech
《Photocatalytic nanomaterials》
- Online mall |
- ENGLISH |
- 中文
Hotline:400-000-9809
Your current location:Home - News - Catalytic combustion treatment of sprayed organic waste gas: discussion of intake air concentration
Catalytic combustion treatment of sprayed organic waste gas: discussion of intake air concentration
|
Contact us
- Phone:400-000-9809
- Mobile phone:13318215621
- Fax:0757-86408626
- Mailbox:[email protected]
- Distribution centres:Six Changfu Urban Creative Industry Park in Luocun, Shishan Town, Nanhai City, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
ISO9001 certification national high and new technology enterprise disinfection products production enterprise hygiene license intellectual property management system certification of guangdong high quality UV lamp, UV germicidal lamp sterilization lamp, household electrical appliances disi
ISO9001认证企业 国家高新技术企业 消毒产品生产企业卫生许可证 知识产权管理体系认证证书
广东优质UV灯,紫外线杀菌灯消毒灯,家用电器消毒灯,高能离子管,UV光催化网,紫外线镇流器
废气处理UV光催化技术方案,废气处理设备光解使用指南,污水消毒应用方案 15019601356 186666550579
2020广东亮月亮光电科技有限公司 版权所有 备案 粤ICP备17031447号 [email protected]
2020广东亮月亮光电科技有限公司 版权所有 备案 粤ICP备17031447号 [email protected]

 About Us
About Us Vision
Vision Corporate culture
Corporate culture Corporate video
Corporate video Service mode
Service mode
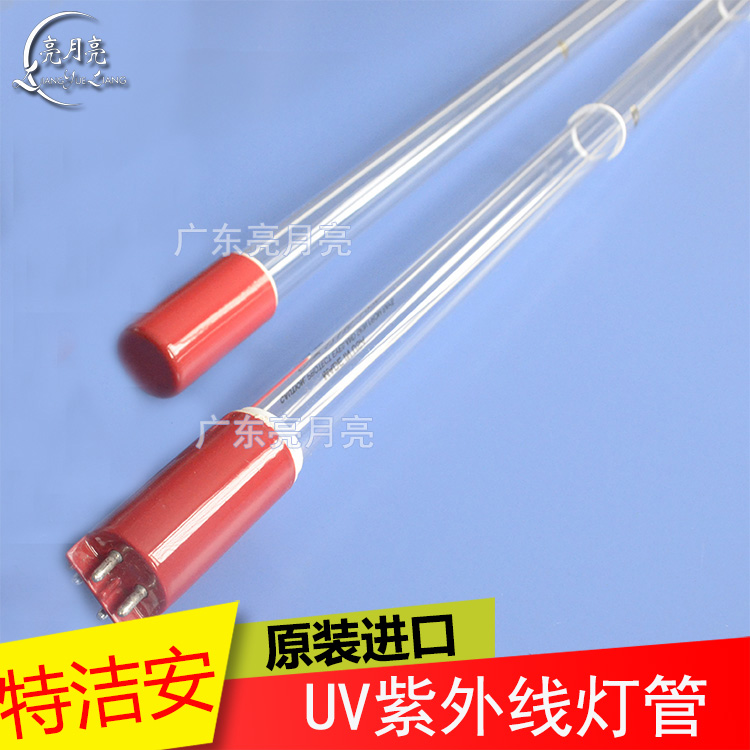
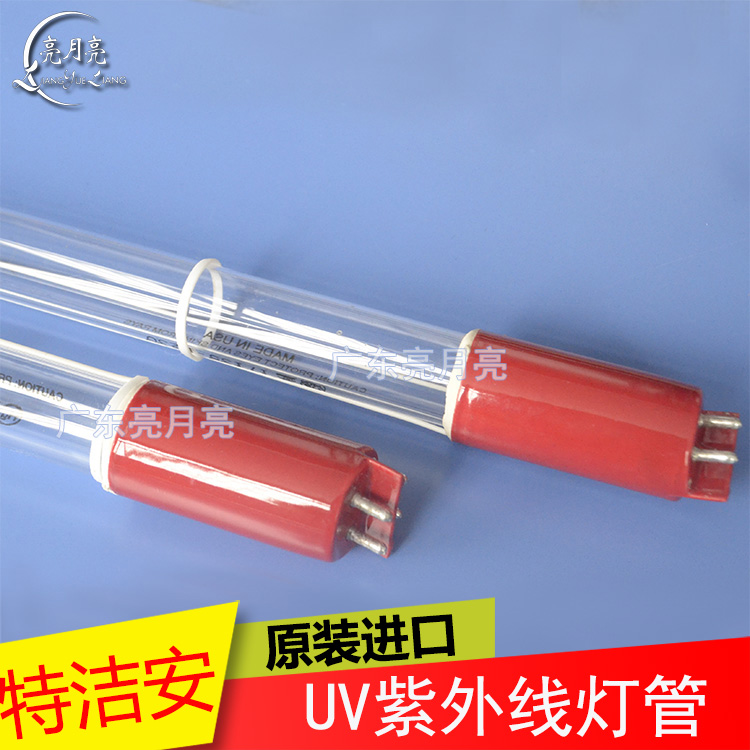
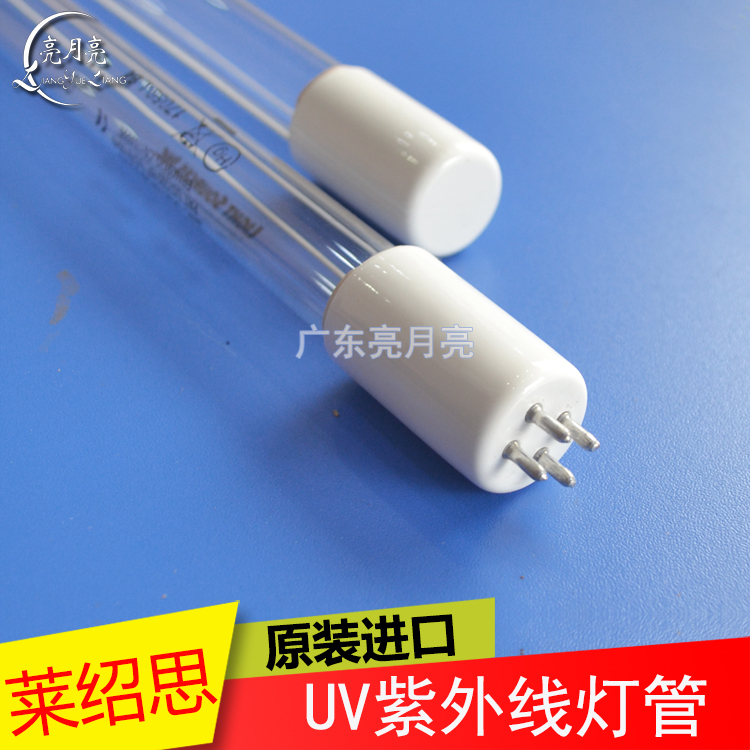
 1554mm waste gas sewage treatment ultraviolet germicidal lamp
1554mm waste gas sewage treatment ultraviolet germicidal lamp Aquarium Aqua UV germicidal lamp
Aquarium Aqua UV germicidal lamp Metal head 100W full submersible water treatment lamp
Metal head 100W full submersible water treatment lamp